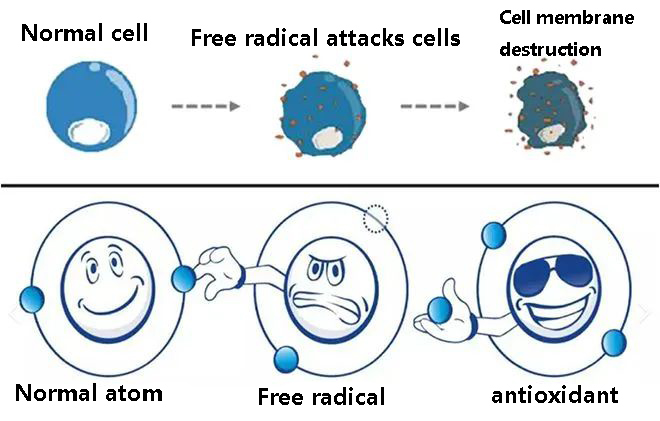
Glutathione has a strong free radical scavenging ability and plays an important role in maintaining the antioxidant balance in the body and protecting cells from free radical damage.
Composition and properties of glutathione
Glutathione (GSH) is a small molecule peptide composed of three amino acids: glutamic acid, cysteine and glycine. It contains sulfhydryl (-SH), which gives glutathione unique antioxidant and free radical scavenging properties.
Machine made
Glutathione scavenge free radicals in the body through several mechanisms
Direct free radical scavenging
Glutathione can directly react with free radicals in the body (such as superoxide anions, hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radicals, etc.) to convert them into harmless substances, thereby protecting cells from free radical damage.
Participate in the antioxidant enzyme system
Glutathione is a cofactor of many antioxidant enzymes in the body, such as glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase, etc.
These enzymes can catalyze the decomposition of free radicals, and glutathione helps these enzymes complete the catalytic process by providing sulfhydryl groups.
Regenerates other antioxidants
Glutathione can also interact with other antioxidants (such as vitamin C, vitamin E, etc.) to regenerate antioxidants oxidized by free radicals, thereby maintaining the balance of antioxidants in the body.
Glutathione scavenging ability of free radicals
Glutathione is a highly effective antioxidant, and its ability to scavenge free radicals is very strong.
It can not only remove free radicals in cells, but also protect biological molecules such as cell membranes, proteins and DNA from free radical damage.
Glutathione can also reduce free radical damage to cells by participating in the detoxification process, converting toxic substances in the body into harmless substances and expelling them out of the body.
Distribution and function of glutathione in vivo
Glutathione is widely distributed in various tissues and organs in the body, especially in liver, kidney, red blood cells and other tissues.
It plays a variety of physiological functions in the body, including anti-oxidation, detoxification, enhancing immunity, protecting the liver and so on.
Apply
Glutathione has a wide range of applications in medicine and health care because of its powerful ability to scavenge free radicals.
For example, it can be used to treat hepatitis, keratitis, cataracts and other diseases; It can also be used as health care products to delay aging, beauty and so on.