With the growth of the global elderly population, scientists are working hard to find ways to slow down the aging process. Among them, the precursor of nicotinamide adenosine dinucleotide (NAD+), nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), has attracted much attention due to its ability to increase human NAD+levels.
In order to meet market demand, manufacturers adopt different methods to manufacture NMN supplements. Among them, chemical synthesis, bacterial fermentation, and enzyme transformation are the most commonly used methods.
1、 Chemical synthesis
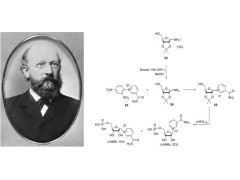
Chemical synthesis is the most commonly used method for manufacturing NMN supplements, but this method is costly and environmentally harmful. Manufacturers typically use zinc based reactions to synthesize NMN.
Firstly, using P-toluenesulfonate as the starting material, two types of NMNs were obtained after a series of chemical reactions: Elephant-NMN and Cat-NMN.
Although this method can produce a large amount of NMN, the waste generated from the use of chemical reagents may pose a threat to human health and the environment.
2、 Bacterial fermentation

Compared to chemical synthesis, bacterial fermentation is a more cost-effective and environmentally friendly method. Through genetic engineering methods, scientists have successfully produced more NMN in bacteria such as Escherichia coli.
During the fermentation process, bacteria use glucose as their energy source and add niacinamide as the starting material for cell production of NMN. This method is not only cost-effective, but also environmentally friendly.
However, the disadvantage of bacterial fermentation methods is that the production speed is slow and requires a longer time to obtain sufficient NMN production.
3、 Enzymatic conversion

Enzyme conversion is an environmentally friendly and efficient method for producing NMN. Our body uses enzymes to accelerate biochemical reactions, so scientists have designed a method that uses enzymes to convert the direct precursor of NMN, nicotinamide nucleoside (NR), into NMN.
However, the problem with this method is that it requires the use of expensive triphosphate as an energy source. Recent studies have shown that supplementing the supply of triphosphate triphosphate by adding additional enzymes can solve this problem.
In enzyme conversion methods, researchers use specific fungal enzymes (such as NRK enzymes) for reactions to produce NMN more efficiently.
Compared with chemical synthesis and bacterial fermentation, enzyme conversion has higher NMN production and more environmentally friendly advantages.
This method is not only more eco-friendly, but also can achieve higher NMN production, thereby reducing production costs and meeting market demand.
Conclusion:
With the growth of the global elderly population, the demand for NMN supplements is also increasing. In order to meet market demand and protect the environment, manufacturers need to choose a production method that is both efficient and environmentally friendly.
Although chemical synthesis is commonly used, it is costly and harmful to the environment; Although bacterial fermentation has lower costs, its production speed is slower; Enzyme conversion has both high yield and environmental advantages.
Through continuous research and innovation, we believe that more environmentally friendly and efficient production methods will be applied in the manufacturing of NMN in the future, making greater contributions to human longevity and health.